DNS, from the English Domain Name System, technically, is a hierarchical and distributed service for computers, services or any resource connected to the Internet that works as a domain name translation system (hosts). for IP addresses. In short, it is through DNS that we can just type a name like www.lumiun.com in the browser's address bar to access the Lumiun website, without having to enter an IP number (200.154.39.214), which is a combination numbers that are difficult to remember.
How does DNS work?

You can access any website on the Internet by its domain name (lumiun.com) or by the IP address (200.154.39.214) of the server where that website is hosted. So that it is not necessary to enter the combination of IP numbers in the browser's address bar whenever you enter the address of a website you want to access, the DNS does the work of translating the name of the domain that makes up the URL, into the IP address of the respective website's server, directing access to that server.
Imagine your contact list on your cell phone. To call someone, simply select the contact's name, then the cell phone translates that name into the phone number and makes the call. DNS works in a similar way.
Each server on the Internet has a unique IP address, so each domain is directed to a specific IP. Therefore, it is not possible for two different websites to have the same addresses (URLs).
There are 13 root DNS servers around the world and without them the Internet would not work. Of these, ten are located in the United States, one in Asia and two in Europe. To expand the installed base of these servers and make the service faster, there are replicas located all over the world, including in Brazil.
Who manages DNS?

For the IP and DNS address system to function correctly, global coordination is necessary, as it is necessary to ensure that it is not possible to assign IP addresses in a decentralized manner and also that each IP address identifies a single server or equipment worldwide.
The organization responsible for managing domain names and IP addresses around the world is ICANN (an acronym for Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers). It is the responsibility of this entity to keep all websites registered and functioning on the internet.
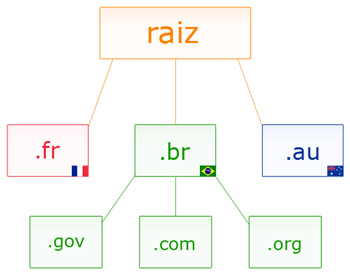
In Brazil, internet addresses are managed by NICBR – PONTO BR Information and Coordination Center . Services and information about domains, address queries and registrations can be carried out at Registro.BR . Brazil has so far (10/15/2020) 4,468,898 registered domains. Updated statistics are available at www.registro.br/estatisticas.html .
How to use DNS?

All equipment connected to a network and the Internet needs a DNS server to communicate on the network and access the Internet. Defining the DNS server is part of the basic network and computer configurations. Known DNS services are generally used, such as Google's DNS (8.8.8.8) or Internet providers' own DNS.
Lumiun Lumiun Box and Lumiun DNS are services that use the DNS system to offer security and access control to the Internet , filtering which domains can or cannot be accessed, according to their indicative classification, improving productivity in companies and also increasing the security of data. You can see in more detail how it works and the benefits and advantages of controlling internet access in corporate environments.










1 comment
Comments closed