Does your company use firewall? How do you protect the borders of your network? Is the protection of the network perimeter important? Let's review some concepts to assist in these issues.
firewall
A firewall is a security device that controls the flow of data on a network. With it, you can filter traffic, configuring what should pass through and what should be discarded. It can be installed between two different networks, between two segments of the same network or even on an end equipment connected to the network.
The origin of the term firewall explains its concept well. The word emerged in the seventeenth century to identify a type of wall, used in construction, whose material prevented the spread of fire. These fire walls, or firewalls, were used to increase the safety of the buildings, preventing a possible fire from being spread to other parts of the building.
When configured correctly on a computer network, Firewall acts as an additional layer of external attack protection and increases the safety of the company's network, equipment, systems and information. Normally firewall is one of the main defenses in the perimeter of a private network, being an essential component in protecting unwanted traffic and invasion attempts.
In Firewall IP, the most traditional structure allows the creation of rules for blocking or release of packets based on characteristics such as protocols (TCP, UDP, ICMP etc.), services (http, https, SMTP etc.), ports (individual, lists or port tracks) and IP addresses and traffic destination, including host addresses, networks and tracks Addresses. You can configure each rule for log generation, if desired, to maintain a record of all locked and/or released connections.
Network perimeter
The internet is an environment with not very explicit borders. You are responsible for understanding the perimeter of your private network and protecting it. If your network has features that need to be externally accessed, it is necessary to accurately control what can be accessed, and from what origin.
The perimeter separates networks with different levels of confidence, such as private internal (reliable) and outer internet (non -reliable) network. You can also separate networks with different functions, user groups or other criteria.
Firewall, being a perimeter protection mechanism, is positioned on its edge: controlling traffic that passes through the firewall, we will be controlling what enters and leaves the protected perimeter.
Why protect the perimeter of the network?
It is unnecessary to say that company networks, equipment, systems, and information need to be properly protected to reduce risk and maintain competitiveness and business continuity. Protection can (and should) be done on each equipment and each system at all levels where this is viable.
The scalability of personal protection of all network equipment and systems involving protocols, services, ports and addresses is the problem. In a network with 5 equipment, not so much. However, in a network with 20 equipment, it is already a challenge.
Computers desktop, notebooks, servers, storage NA, Android smartphones, iPhones, TVs, surveillance cameras - are you sure all these equipment is 100% exempt from vulnerabilities and closed against invasion or abuse? This would not be possible. And this is one of the main reasons that make the protection of the network perimeter a very relevant security measure.
Currently, protecting equipment connected to the network is as essential as seeking the protection of business information. To protect business information it is necessary, among other things, to protect the equipment and systems that store and process this information.
Network -related equipment, operating systems, internet browsers and other software components have vulnerabilities. Many already corrected, many to be unveiled, exploited and abused, increasingly faster, even before the developer or manufacturer elaborates and distributes the respective correction.
The perimeter firewall prevents unwanted external traffic from crossing the edge of the network and accessing potentially vulnerable internal network systems and equipment, which would characterize an invasion. Similarly, it prevents internally originally originated connections from accessing prohibited external resources, depending on the implemented settings.
Although much of the work and business information is currently in the cloud - usually in protected environments - it is also necessary to protect the equipment that access this information. While the devices used for access are within the company's private school perimeter, protecting them is a company's responsibility in its IT management. A firewall for network border protection is a feature that usually offers an additional protection layer.
An example of exploration of equipment vulnerabilities is Botnet called Satori, also known as Mirai Okiru, which invades equipment connected to the internet and has control over them, forming a gigantic network of remotely controlled “zombies”. With this, Botnet gets a large processing and connectivity capacity, and can be used to send spam mountains or massively attack a site until it knocked it. Botnet Satori, very active in 2018 and with relevant presence in South America, takes advantage of two vulnerabilities: CVE-2017-17215, whose attack is directed to door 37215; and CVE-2014-8361, with attack on port 52869.
Infected equipment becomes a zombie and looks for its own network by other vulnerable equipment so that it can spread malware and expand Botnet.
But the question is: What Firewall solution should I use on my network?
Below are some firewall solutions aimed at corporate environments, and we believe we are valid to analyze functionality and values, according to your business needs.
Firewall Solutions
Currently the main network firewall solutions offer complementary features that go beyond the packet filter which is the Firewall IP itself. Features such as load balancing (to use multiple internet links), VPN connections (for secure remote access to the company network) and webfilter, or web filter, are offered to control which websites are allowed and which sites are blocked, by security and productivity measures.
As a way of exemplifying firewall solutions, follow examples of the firewall configuration interface in different solutions. The focus at this time is the configuration of IP firewall , ie the packet filter that controls traffic between networks based on protocols, services, ports, origin IP addresses and destination.
Fortigate
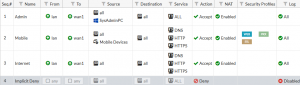
Fortigate solutions
Sonicwall
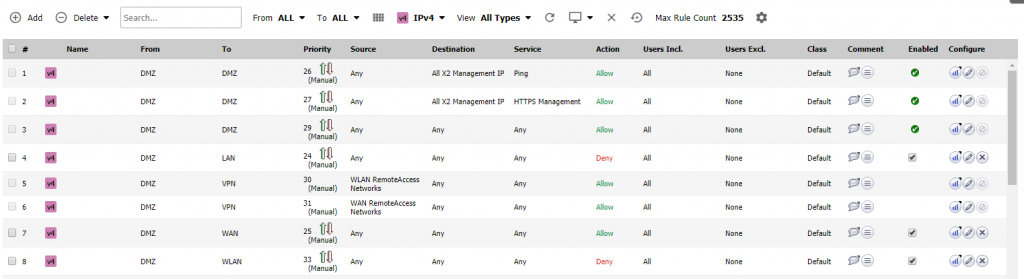
See more about Sonicwall solutions
Lumiun
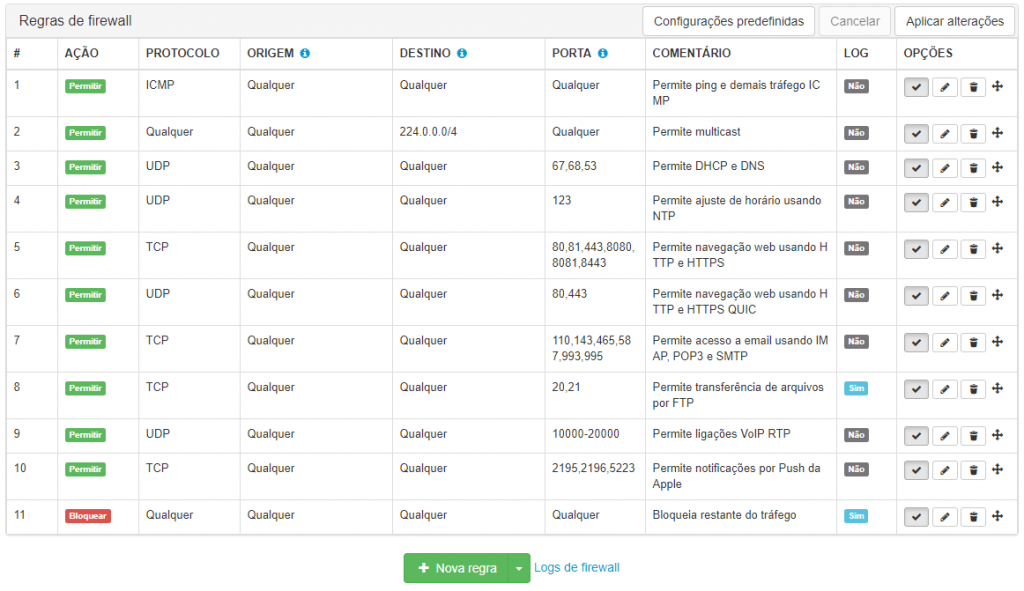
See more about Firewall Lumiun
Sophos
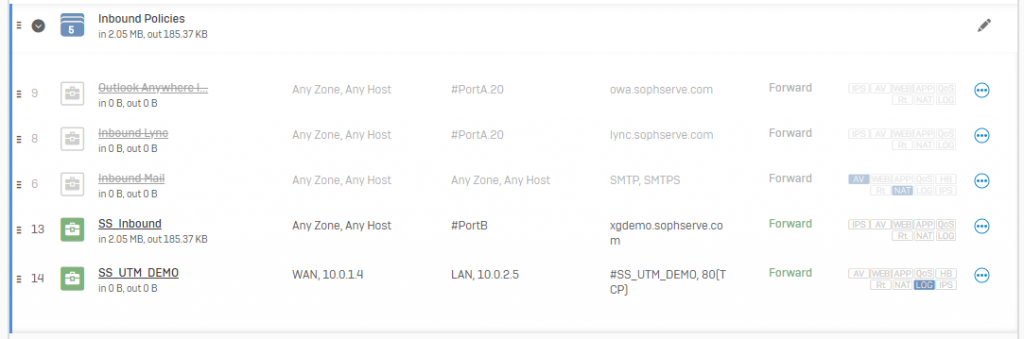
See more about Firewall Sophos
pfSense
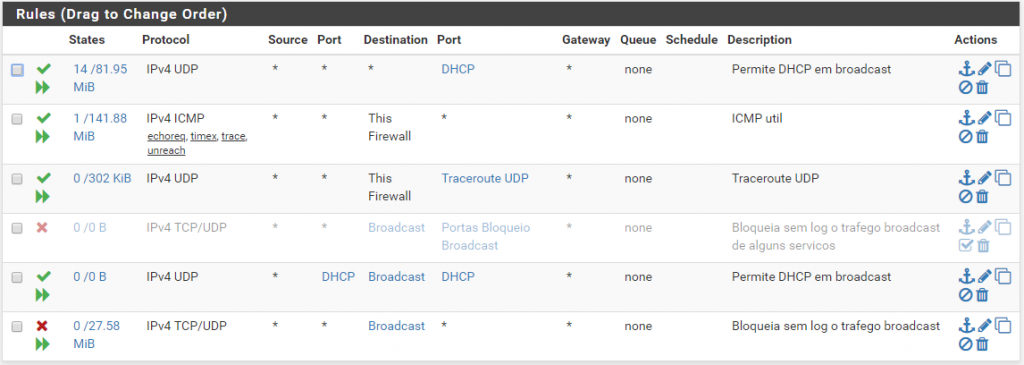
See more about the PFSense solution
Linux iptables
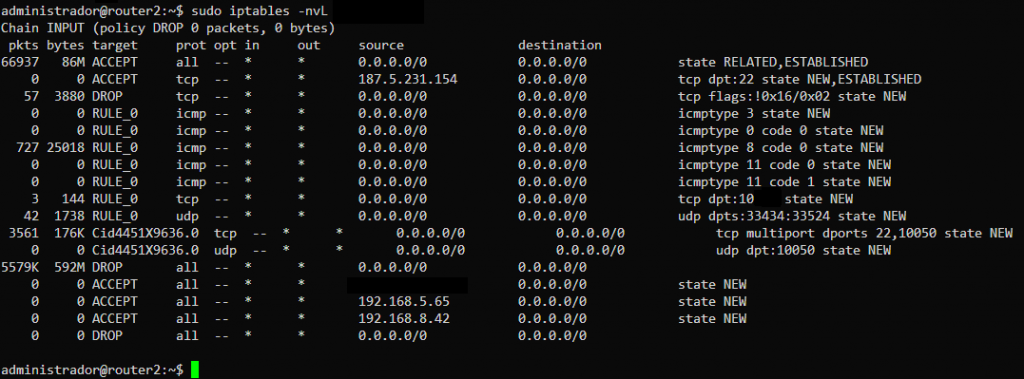
See more about Netfilter and Iptables
Conclusion
Yes, your network needs protection of a firewall on the border with other unriviable networks, such as the internet.
Unless: in this network there is no equipment; or that these equipment and their systems are permanently exempt from vulnerabilities (both old and those not yet discovered); And in this network circulate only information whose loss or publication is irrelevant - in this case, it does not need firewall.
Therefore, it is understood that it is usually important to have the protection of a properly configured firewall in your network.
It is up to those responsible for business management and information technology to adopt, maintain and revise actions aimed at protecting business information. Protecting the perimeter of the company's network is an important action for network security and information that travels in it.
For the implementation of a new firewall on the network, precisely and effectively, with fewer inconvenience and less complications, seek to understand which solution is best suited for your size and business profile. Resources such as predefined configuration policies, firewall rules models, cloud panel management and permanent technical support, which are offered by some solutions, can make a lot of difference in the implementation and operation of the solution with safety and reliability.
Until later!












6 Comments
Comments closed